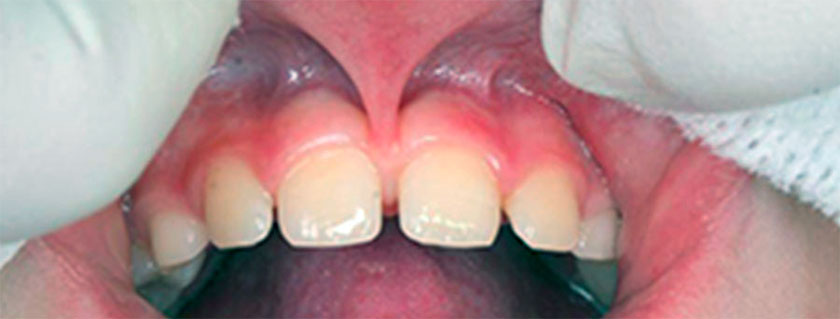
Frenulum; It is a soft mucous tissue, which is located between the gingival tissue and the tongue, lips and cheeks, and at the same time binds these tissues to each other and limits their movements.
Frenulum is a feature that varies from individual to individual. Everyone is also under the tongue. It is found more than once in the posterior region of our lower and upper front teeth and on the cheek. It also varies from person to person.
When frenulums that cause gum disease are larger and thicker than normal, and when they are attached too close to the edge of the tooth, they can pull the gum down and cause gum recession and gum disease. Because it pulls the gum down and gum recession is experienced. This can cause speech problems and cause great discomfort, especially in young children.
At the same time, if there is a frenulum that is thicker than normal and larger than normal between the lower, upper and middle teeth, it causes the teeth not to come together and creates an aesthetic problem because of the gaps called diestema between the teeth.
If frenulums are close to the gingival margin, which may cause gingival recession and gingival disease, they should be removed from that area. When they are located between the upper and lower incisors and cause diastema, the frenulum should be removed first, and orthodontic treatment should be continued to bring the teeth together.
Thanks to the technology developed with a process called frenulum frenectomy, the result can be achieved in a very short time with the help of laser. However, in cases where the ligament is too large or deep, it must be surgically removed and sutured. There is no scar after frenectomy.
This procedure has no effect on speech, and there is no change in the appearance of the teeth after phenectomy.